The task of trading and investing is to profit from the price fluctuations of various assets. Trading and investing always involve risks, and capital is the instrument used. Protecting capital is of paramount importance, and the goal of a trader is to choose the least risky and most profitable trading strategy.
To strictly adhere to a trading strategy, market participants can place an order to buy or sell a financial asset at a specific advantageous price. Such orders are called limit orders.
The main feature of a limit order is that the transaction is only opened when the asset reaches the price specified in the order.
Limit orders can be divided into two types:
- Buy or sell orders are used to open trades at the most attractive price.
- Stop orders are used to forcibly close a position in order to reduce losses.
Let us consider how a limit order is placed using the example of the Bitbanker platform trading terminal. Say we are buying Ethereum with the intention of selling later at higher prices.
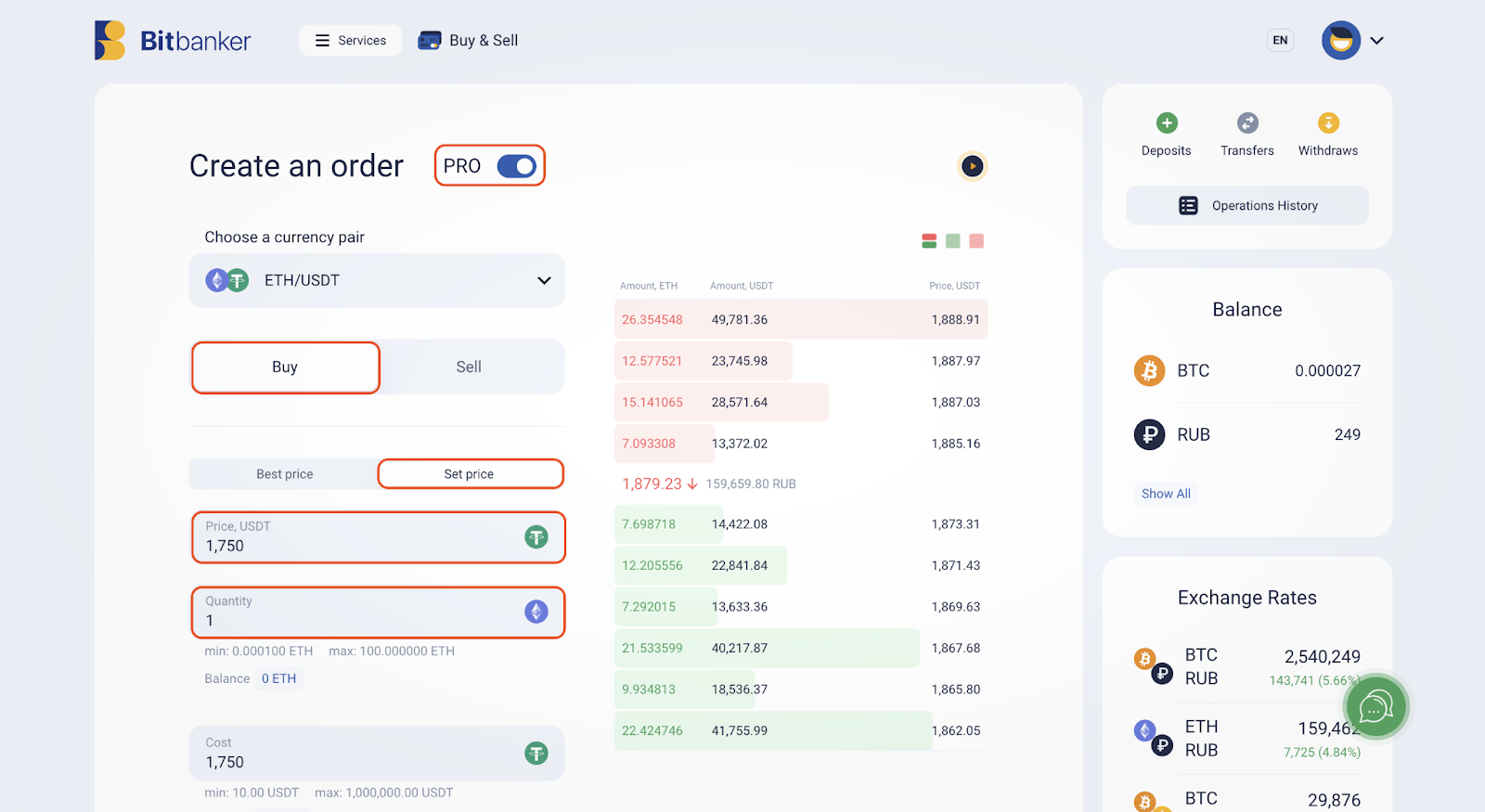
The Mandatory Parameters to Fill When Placing a Limit Buy Order
The two main parameters of a limit order are:
- The desired price.
- The quantity of the asset to be bought at the chosen price.
To place a limit order, we need to go to the “Buy and Sell” section of the platform’s services and switch to PRO mode.
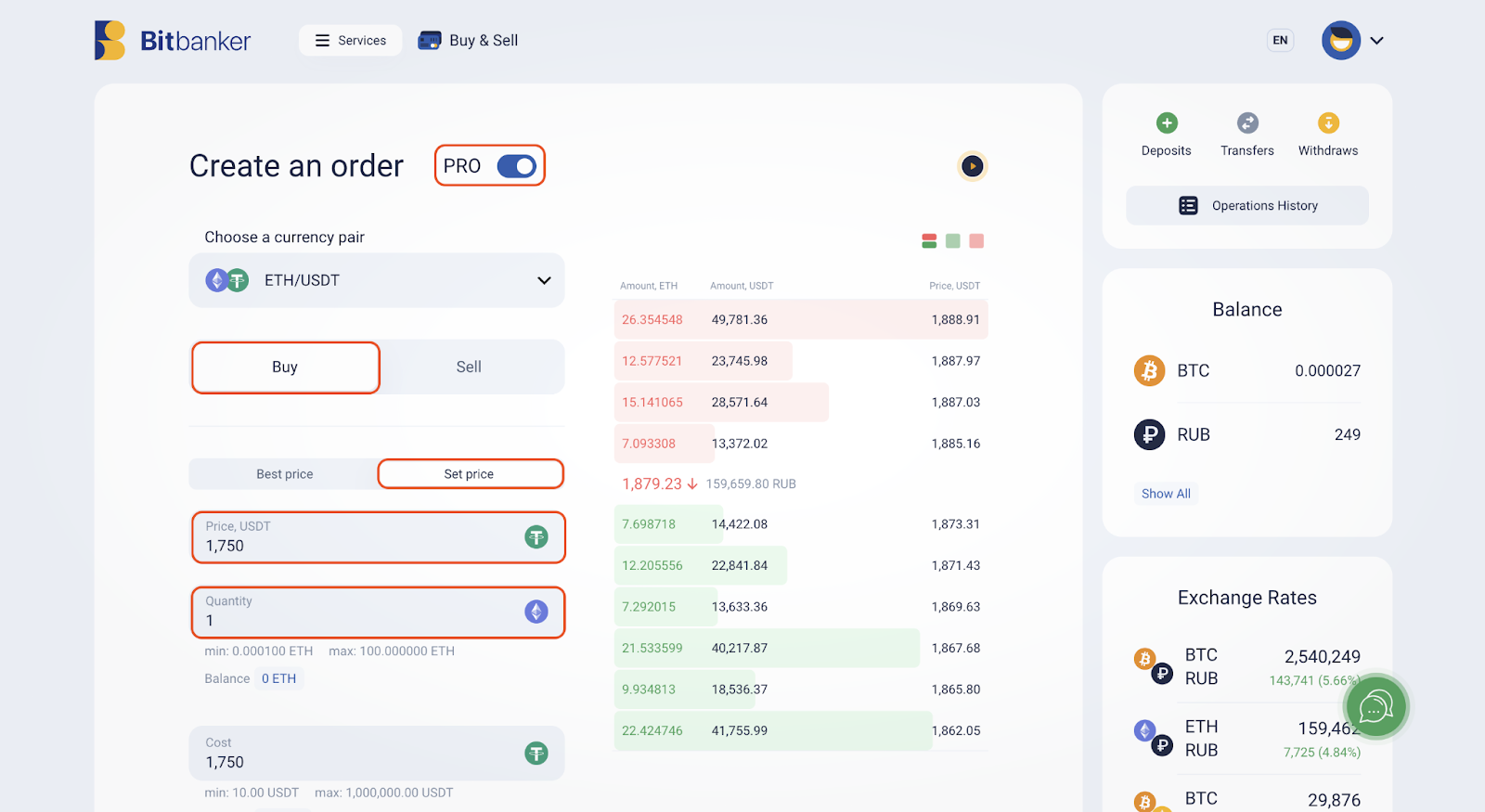
In our case, we are considering buying 1 ETH at a price of 1,750 USDT. This price differs from the current market value of the asset, which is 1,879 USDT at the time of placing the order. If ETH drops to the $1,750 level, our order will be automatically executed.
Advantages of a Limit Order:
- A limit order allows one to enter a trade when the asset reaches the desired price, without the need for constant monitoring of the selected instrument.
- A limit order helps reduce the size of the commission. Users trade as makers, meaning they provide liquidity with their orders, rather than as takers who utilize liquidity. Usually, the fees for makers on trading platforms are lower than for takers.
- After a limit buy order for 1 ETH is triggered, a limit sell order can be used to profit from the trade. To do this, it is necessary to determine where the nearest block of sellers will be located. In our case, it makes sense to exit the position when the price reaches the psychological level of $1,900. Previously, the asset fell below $1,900, indicating that this price will act as a resistance level for an upward movement.
To place a limit sell order, the following details need to be specified:
1. The limit price at which the order will be placed.
2. The quantity of the asset to be sold at the limit price.
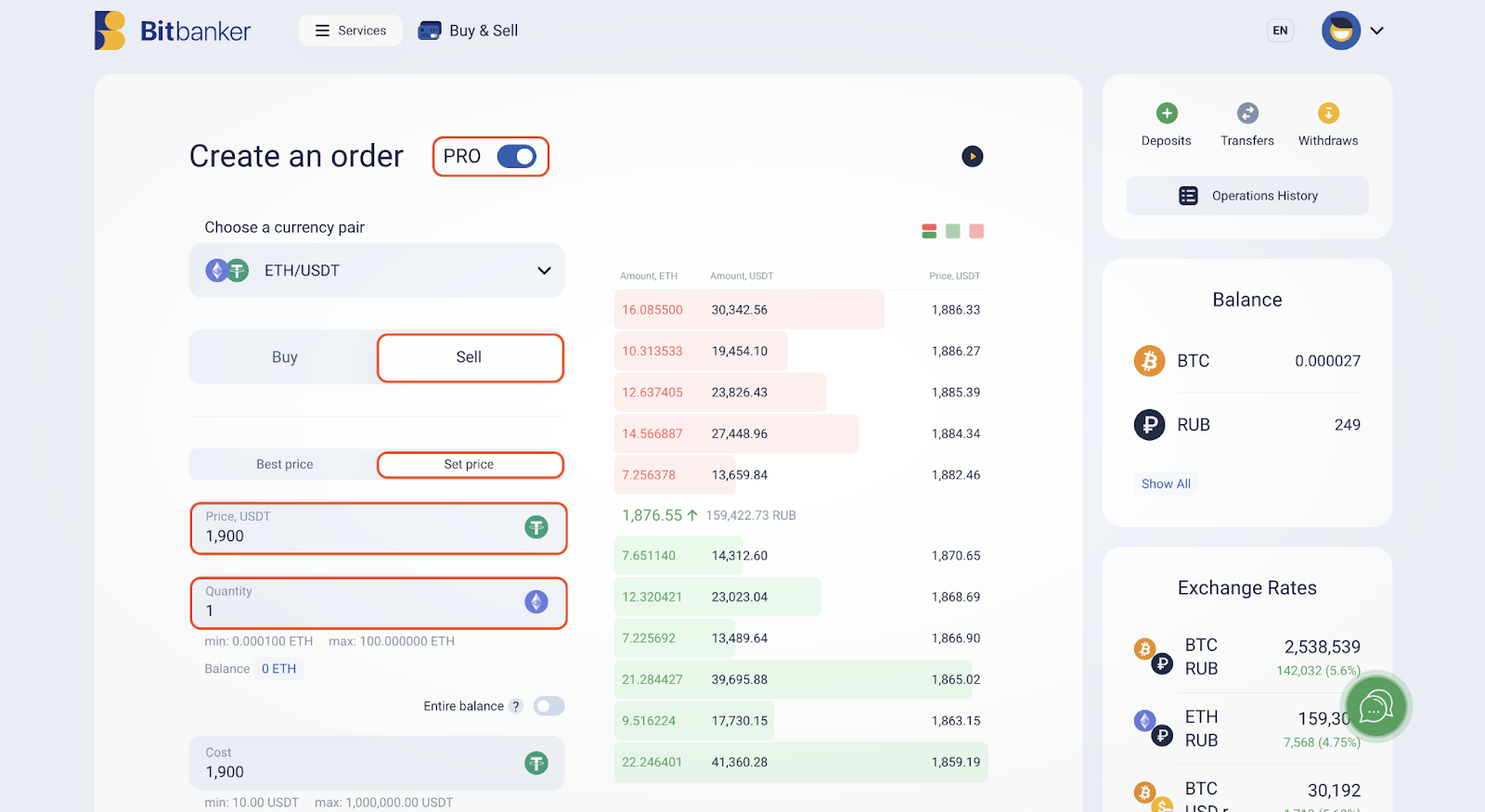
According to the set limit order, we will sell our asset when ETH reaches the 1,900 USDT mark and there is sufficient buyer demand for it. Thus, a limit order allows us to automate our trading and remain free from monitoring prices 24/7.
In general, a limit order serves as protection against slippage, which is the execution of an order at a price worse than the specified price at the time the order was added to the order book. This is particularly relevant in highly volatile cryptocurrency markets. For example, a trader uses a market order to buy an instrument whose price is rising, and the order is placed for an amount exceeding the current limit sell orders at the lowest price. As a result, the remaining part of the buy order will be executed at the next available limit sell order at a higher price.
As a result, the trader will acquire the financial asset at a higher price than the one stated in their initial order, resulting in lower potential profit.
Disadvantages of a Limit Order:
- A limit order is only executed when the asset reaches a specific price. There is always the possibility that the order may not be executed if the market exchange rates of the financial instrument do not reach the specified values.
- Limit orders are placed in the order book in chronological order. Orders with the same price will be executed based on the time they were added to the trading platform. A limit order is usually placed for a period of several months, but this depends on the specific cryptocurrency exchange.
- In a market with low liquidity, a limit order may be only partially executed. For example, the order may be filled only for 20%, which reduces the potential profit.
When Is It Better to Use a Limit Order?
- When buying or selling an instrument at a price different from the market price. For example, when the instrument reaches levels of buyer or seller support.
- When the trader can wait for the desired price. The waiting period can last for months.
- To split a large order into smaller limit orders to average the dollar cost of the open position.
How Does a Limit Order Differ from a Market Order?
A market order allows for instant buying and selling of financial instruments at the current market price. Unlike a limit order, the price of the asset is not specified in a market order; only the quantity of the asset is indicated. Market orders rely on the prices of limit orders in the order book, so in case of insufficient liquidity, the purchase or sale of the asset may occur at a less favorable price for the trader, resulting in slippage, as mentioned earlier.
The main advantage of market orders compared to limit orders is the swift opening of a position, which is important when trading on breakout levels of resistance or support, as well as when an asset breaks out of technical analysis patterns. Market orders can be actively used in scalping, which is a type of intraday trading. Using limit orders can be challenging during periods of increased market volatility.
A trader may also resort to a market order if a limit stop order is not executed and an immediate purchase or sale of the instrument at the market price is required to rectify the situation. However, exchanges usually charge higher fees for executing market orders compared to limit orders.
Market orders should only be used when the risks of price slippage and high commissions are insignificant compared to the benefits of immediate position opening.
Limit Orders and the Order Book
Placing limit orders to buy and sell a financial asset provides an understanding of the overall balance of forces on the market and indicates areas of liquidity accumulation. Ultimately, this provides an understanding of trading levels from which a price reversal may occur.
The order book is a panel on a trading terminal that displays limit buy and sell orders from all traders participating in the market at that moment. Let us consider the order book for the ETH/USDT cryptocurrency pair on the Bitbanker trading platform as an example.
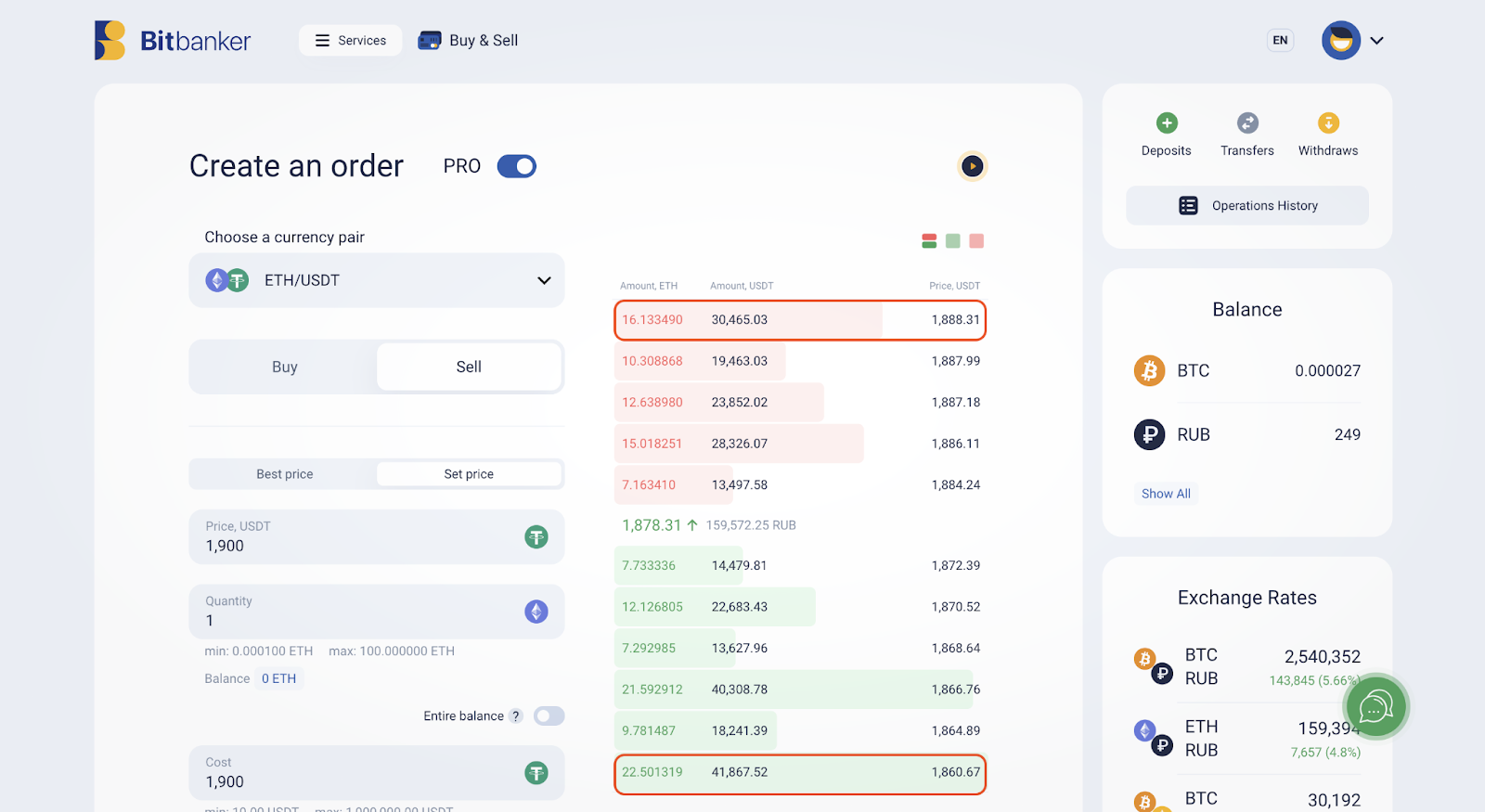
As we can see, there is a significant accumulation of sell orders at the $1,888 level. This level acts as resistance for the asset, and when it is reached, there is a higher probability of a price retracement.
On the other hand, large buy orders are located at the $1,860 level. This indicates buyer interest at that trading level, suggesting it could serve as a support level. If ETH retraces to this level, a price reversal may occur, and the asset’s value may start rising due to increased demand for it.
The order book should be used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools and should not be relied upon solely. In most cases, limit orders are not static and correlate with the market price of the asset.
Market Manipulation Using Limit Orders
In the case of low-liquidity assets, large market participants can influence prices by placing limit orders. For example, in a declining market, they can create large sell orders to deter buyers. Such an order is placed to lower the price to more advantageous levels for the large player or to prevent it from rising before their subsequent purchase.
On the other hand, in a rising market, a manipulator can place a massive buy order for the financial instrument to attract additional buyers and facilitate the execution of their accumulated position. Therefore, it is important to have an understanding of the order book and be able to track the change in the ratio of limit orders over time to understand the current market sentiment and adjust trading strategies accordingly.
