A market order is a request to buy or sell an asset at the current market price. When placing a market order, a trader can only specify the quantity of the cryptocurrency involved in the transaction, as its price will be determined by the current ratio of supply and demand.
Types of market orders:
- Buy or sell order at the current market price.
- Stop order for forced position closure at the market.
The second type of order has a twofold nature. The closing of a trading position at the market price occurs when the stop price is reached.
Is a Market Order Executed and How Is It Related to Limit Orders?
A counteroffer from another party is required to execute a market trade immediately. Liquidity for executing a market order is provided by previously placed limit orders, which are displayed in the order book of the exchange.
Many exchanges categorize traders as makers and takers:
- Makers are traders with limit orders to buy and sell cryptocurrencies at their desired prices. These prices differ from the market price, so they are not executed immediately.
- Takers use market orders to enter trades. They fill the orders created by makers and take liquidity from the platform. Many exchanges incentivize makers for providing liquidity by reducing their trading fees.
Let us consider how to create a market order on the Bitbanker platform. Please note that the specific actions for buying or selling cryptocurrencies depend solely on your chosen trading or investment strategy. Assume that we are interested in purchasing BTC. We will have to navigate to the “Buy and Sell” section of the service, use fast purchasing, or switch to the PRO mode, and find the following trading terminal:
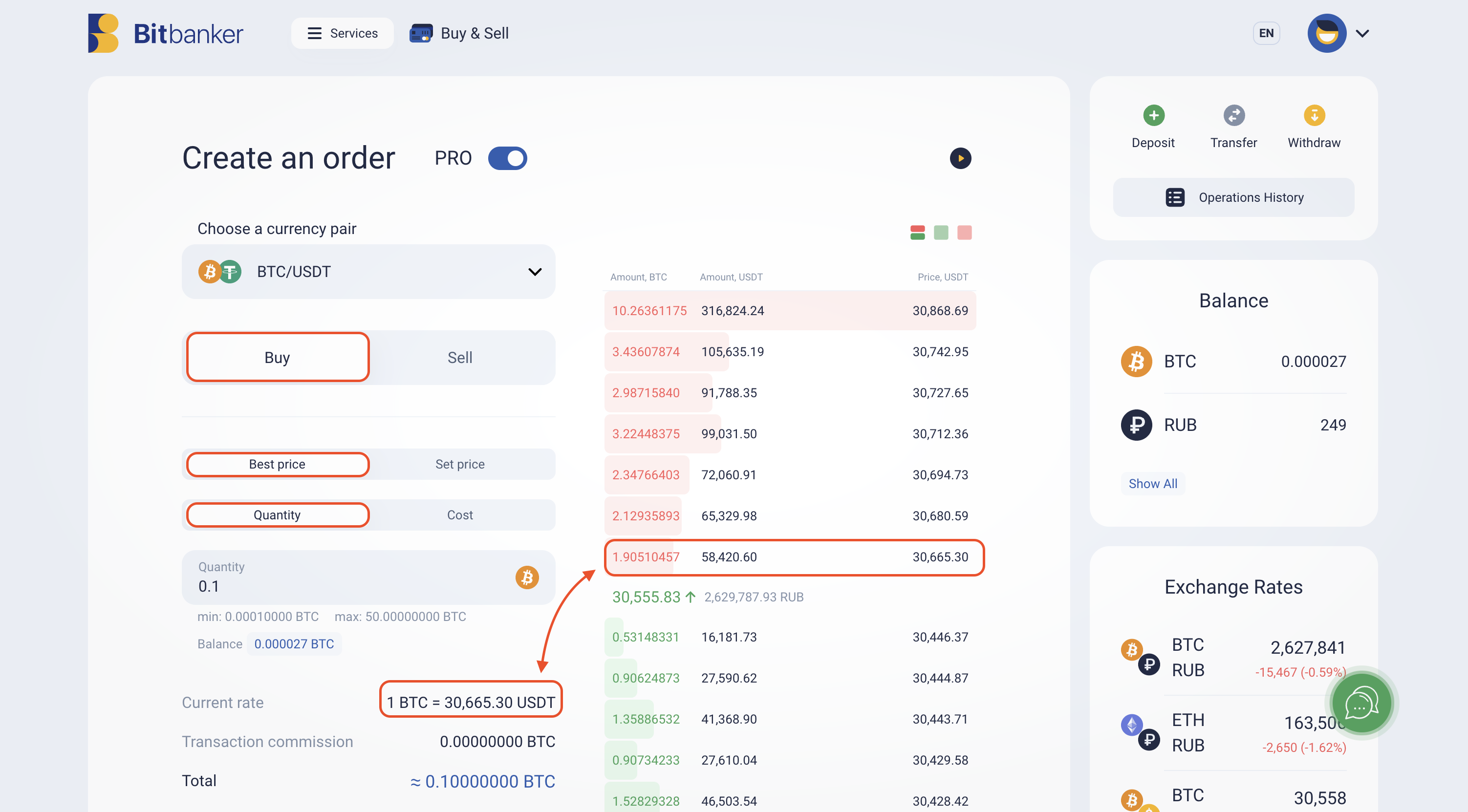
To create a market order, you need to select the “Best price” tab and specify the amount of the asset you plan to purchase. In our example, the amount is 0.1 BTC. As we now know, market orders are executed based on the liquidity of the limit orders placed. Accordingly, the price of our purchase at the time of placing the market order will be 30,665.30 USDT. This will be the best market offer for us.
Suppose we needed to buy more Bitcoin than the limit order for sale at the best market price offers, i.e., more than 1.905 BTC. When a market order exceeds the supply of the most accessible limit order, the remaining quantity of cryptocurrency will be automatically matched by the exchange with other limit orders for sale at prices closest to the market price. This process of changing the execution price of a market order is called slippage.
In our example, the remaining amount of BTC from our order would be purchased at a price of the next offer, which is 30,680.59 USDT. Due to a lack of liquidity, we may buy Bitcoin at a higher price compared to its cost at the time of order placement. It is important to keep this characteristic of market buying in mind when opening a position.
For quick buying or selling, you can skip going to the Pro section and immediately place an order at the current price after switching to the “Buy and Sell” service.
Advantages of a Market Order:
1. Ease of use: Market orders only require the user to specify the quantity of the financial instrument involved in the transaction.
2. Execution speed: Market orders provide near-instant market entry. This is important during rapid changes in the local trend or breakthroughs of key resistance or support levels.
3. Transaction execution guarantee: This is particularly important when placing a stop order, where the position will be closed at the market price rather than the limit price, as it reduces the risks of potential losses if the market moves against the open position.
Disadvantages of a Market Orde:
1. Lack of control over the desired price: The transaction is executed at the market price at the time of entering the position, making it difficult to plan transactions in advance. Traders need to constantly monitor the market and control their trading activities.
2. Price slippage risk: Market participants may pay more or receive less due to insufficient liquidity in limit orders.
3. Higher trading fees compared to placing limit orders: In most cases, exchanges charge higher fees for market orders. This is done to incentivize market makers who provide liquidity for transactions.
How Is a Market Order Different from a Limit Order?
A market order differs from a limit order primarily in terms of execution speed. You can quickly enter or exit a position during high market volatility. This requires specific trading skills from the trader and constant monitoring of the market situation.
On the other hand, a limit order allows you to wait for a more favorable price to buy or sell a financial instrument. It frees the trader from the need to constantly observe market conditions. Market participants can identify the most interesting entry and exit points in advance based on the readouts of technical analysis tools and wait for the asset price to approach the desired level.
When Is It Better to Use a Market Order?
1. When you need to join the price movement immediately.
2. When manually closing a position that has lost its relevance as a trading idea.
3. Best used for highly liquid assets to reduce the risk of order slippage.
4. Can also be used for long-term investments when intraday price fluctuations can be disregarded.
Using a market order is advisable when the risk of price slippage and higher commissions is insignificant compared to the advantages of immediate position opening or closing.
What Determines the Choice of Order Type?
All trader transactions on a cryptocurrency exchange are conducted by placing orders. It is therefore important to understand which types of orders are best used to maximize profits.
The choice of order type is influenced by several factors:
1. Trading strategy and trading style.
2. The trader’s experience.
3. Market conditions (volatility, liquidity).
4. Acceptable risk level.
For example, for day traders, opening a position with a limit order can provide additional profit due to lower fees and a more favorable entry point. Market orders are best suited for trading at breakouts of key resistance or support levels. They allow quick entry into the market and provide a chance to capitalize on price movements.
Using a stop-loss order with market closure would be a logical choice if a market participant engages in positional trading with multiple financial instruments. This approach protects against additional losses associated with the possibility of a limit stop-loss order not being executed.
Thus, different types of orders are designed to address specific objectives in each individual situation, which will be determined by a combination of factors mentioned above.
