High volatility is one of the main struggles cryptocurrencies deal with. Volatility complicates the widespread use of digital assets in everyday operations. We need stablecoins to address this exact issue.
DAI is the largest decentralized stablecoin. It is developed by the MakerDAO protocol and operates on the Ethereum blockchain.
DAI is overcollateralized with cryptocurrency, and its value is maintained by smart contracts.
As of the beginning of March 2024, the issuance of DAI amounts to approximately $5 billion. It is the third largest stablecoin, trailing only USDT and USDC.

The DAI exchange rate has shown high stability:
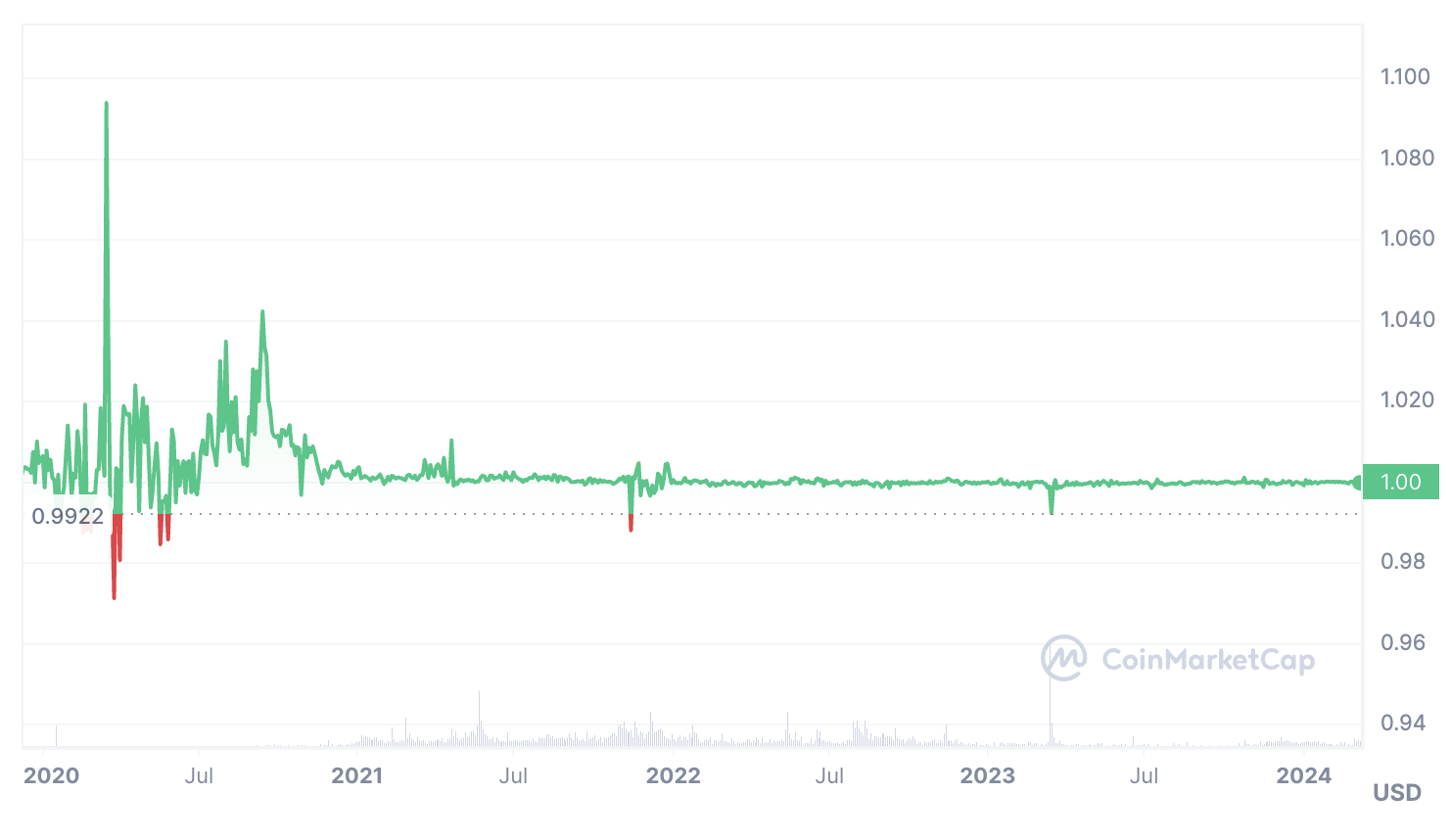
DAI is traded on all major decentralized and centralized exchanges: Binance, Kraken, Uniswap, KuCoin, etc.
History of DAI
DAI was created as part of the MakerDAO project, which was launched in 2015. MakerDAO was founded by Rune Christensen and Nikolai Mushegian. The idea was to create a decentralized stablecoin managed by the user community and independent of traditional financial institutions.
The first version of DAI was called Single-Collateral DAI (SAI) and was launched in December 2017. At that time, only one collateral asset, the Ethereum (ETH) token, was used to back the value of DAI. In November 2019, the project transitioned to Multi-Collateral DAI (MCD). This allowed for the use of various cryptocurrency assets as collateral and increased the diversification and stability of DAI.
In DeFi, DAI has become one of the main stablecoins. It is used for loans, staking, and payments.
DAI Collateralization
Centralized stablecoins are backed by bonds and traditional currencies held in bank accounts. In contrast, DAI is collateralized by cryptocurrencies on the Ethereum blockchain. These can include Ethereum (ETH), Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), USDC, and so forth.
The collateral assets are used to create Collateralized Debt Positions (CDPs) within the MakerDAO ecosystem. To borrow DAI stablecoins, one must lock cryptocurrency in the CDP smart contract.
Users deposit collateral into Maker Vaults and mint DAI stablecoins. Multiple cryptocurrencies can be used as collateral simultaneously. When a user repays DAI, the Maker Vault burns them.Information on DAI collateralization is publicly available via this link.
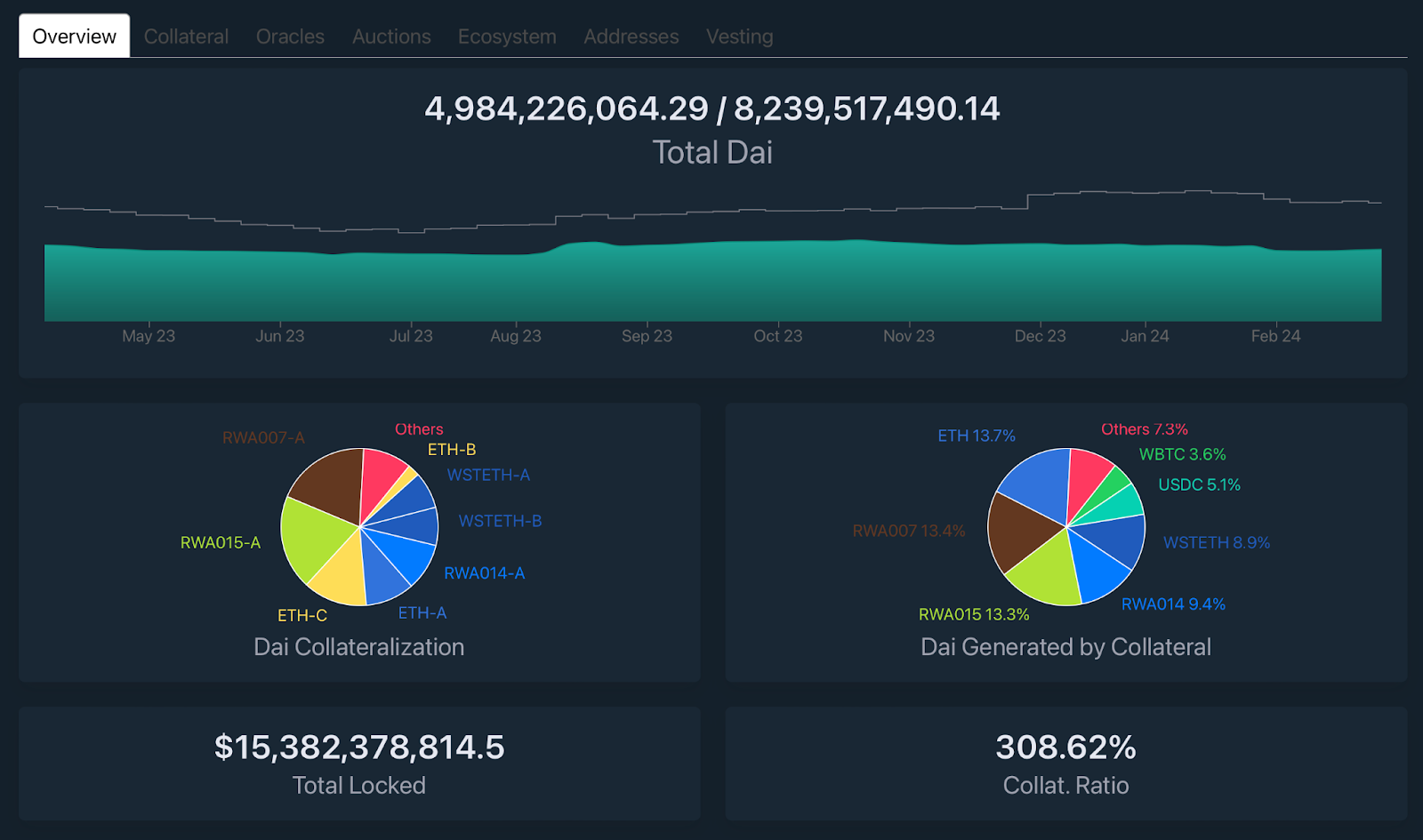
To maintain the stability of the DAI exchange rate against the US dollar, mechanisms such as automatic liquidations and stability fees are used. If the value of collateral assets decreases and the level of DAI collateralization falls below the minimum acceptable level, the collateral assets may be automatically sold at auctions to cover the debt and maintain the stability of DAI.
Why Does the DAI Exchange Rate Remain Stable?
When the value of DAI falls below $1, the system incentivizes users to repay their debts, return collateral, and burn DAI. This is achieved by increasing the stability fee, making borrowing less profitable. The DAO (decentralized autonomous organisation running the project) can also raise the DAI savings rate, increasing demand for the token.
When the DAI exchange rate rises above $1, the stability fee decreases. As a result, the overall supply of DAI increases, and the price of each token decreases. MakerDAO can also reduce demand for the DAI token by lowering the savings rate. This prompts investors to seek alternative income-generating methods.
Usage of DAI
- Payments: DAI is used for instant and reliable payments with low fees.
- Investments: Many diversify their cryptocurrency portfolios by investing in DAI.
- DeFi: DAI is used in many DeFi projects for lending, staking, farming, and other financial services.
- Trading: DAI is used for trading on centralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
- TradFi: DAI is used to a limited extent in traditional finance. Last year, Société Générale raised $7 million in DAI through a loan from MakerDAO. Approval was also granted for the creation of a storage facility with a $100 million limit in DAI for the American Huntingdon Valley Bank.
Pros of DAI
- Decentralization: DAI is less vulnerable to regulatory attacks.
- Transparent collateralization: The collateralization of DAI can be verified by anyone at any time.
- Impossibility of freezing: USDT, USDC, and other centralized stablecoins can be frozen even in non-custodial wallets. With DAI, this can only be done by the MakerDAO community’s decision.
Cons of DAI
- Vulnerability to cryptocurrency market volatility: DAI itself is stable, but the assets backing it can be highly volatile.
- Complexity: The mechanisms for stabilizing and managing DAI are complex to understand, especially for beginners.
- Smart contract risks: All DAI operations are based on smart contracts, and the management is decentralized. In the event of a hack, decentralized projects are more difficult to protect.
- Lower liquidity: The issuance of DAI is much lower than that of USDT and USDC.
Future Outlook for DAI
The most important feature of DAI is its decentralization. The cryptocurrency market urgently needs decentralized stablecoins. As pressure from regulators on centralized stablecoins increases, DAI’s popularity may grow.
Wallets Supporting DAI
DAI can be used on any wallet that supports ERC-20 tokens:
- MetaMask
- Trust
- Atomic Wallet
- Exodus
- AlphaWallet
