A Glimpse into the History of TRC-20
Ethereum, introduced in 2015, pioneered the concept of smart contracts. But it was not until the “DeFi summer” of 2020 that these contracts truly gained traction. As a consequence of its surging popularity, Ethereum faced scalability challenges—resulting in transaction delays and soaring transaction fees during peak periods. This paved the way for alternative platforms like TRON.
In May 2018, TRON’s main network was unveiled, bringing forth the TRC-20 standard. Notably, many parallels can be drawn between TRON and Ethereum. For instance, both utilize virtual machines for executing smart contracts. TRON’s variant, the TRON Virtual Machine (TVM), even employs Solidity—the same programming language used by Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM).
Such compatibility ensures that smart contracts on TRON can seamlessly operate alongside Ethereum’s. TRON’s creators, in fact, intentionally designed their system to simplify the process of transferring decentralized applications from Ethereum to their own platform.
Considering this, one might question: What advantages do developers reap from such a migration?
- TRON boasts superior throughput, vital for scaling solutions.
- Complex smart contract protocols demand more computational power, escalating costs for users. However, TRON’s reduced transaction fees grant developers the leeway to design intricate contracts without imposing excessive fees on users.
TRC-20 Smart Contracts Functions
TRC-20 smart contracts standardize core attributes of tokens, such as their transferability, issuance, and circulation on the TRON blockchain. Notably, transaction fees for these activities are settled in TRON’s flagship cryptocurrency, TRX.
Key Features of TRC-20 Smart Contracts Include:
- Token Issuance: Empowering users to create their tokens on TRON.
- Token Burning: Facilitating the intentional removal of tokens from circulation based on user actions.
- Coin Freezing: Temporarily suspending operations linked to a specific contract.
- Defining Token Ownership Parameters: This determines stakeholders’ interaction levels with a contract post-deployment, ensuring decentralized control by permitting token issuers to relinquish ownership rights.
How does TRC-20 differ from ERC-20 and BEP-20?
While the ERC-20 standard inspired the creation of both TRC-20 and BEP-20, each standard has unique attributes owing to its specific blockchain framework. All three enable the creation and transfer of tokens within their respective protocols.
| Blockchain | Tron (TRC-20) | Ethereum (ERC-20) | BNB Chain (BEP-20) |
| Decentralization Level (Active Validators) | 27 | 960,658 | 29 |
| Average Transaction Speed | 3 secs | 13 secs | 3 secs |
| Average Transaction Fee | $0.14 | $12 | $0.20 |
| Average Daily Transactions in the Last Month | 7 million | 1 million | 4 million |
| Number of Network Apps with a Balance Over $0.1 million (Dapp Radar Data) | 10 | 229 | 161 |
As evident from the table, the TRON blockchain is in particular demand among users. This is indicated by its record daily transaction numbers when compared to its competitors. Furthermore, the introduction of the USDT stablecoin on TRON in 2019 added to its appeal. As per DeFi Llama analytics, around half of the USDT’s total circulation occurs on TRON.
However, TRC-20 isn’t without shortcomings—there’s limited developer activity, and in terms of applications, it trails behind Ethereum and BNB Chain. TRON’s high degree of centralization, with just 27 validators, is also a point of contention.
TRC-20 Tokens: Pros & Cons
Benefits:
- Robust support for decentralized applications.
- Capability to issue fresh digital assets rooted in TRC-20.
- Enhanced code flexibility for developers.
- Quick transaction processing.
- Affordable transaction charges.
- Provision for fee-less transactions, complete with comprehensive guidelines.
Drawbacks:
- Predominant centralization within the TRON framework.
- Limited decentralized applications in contrast to premier networks.
- Repeated regulatory scrutiny targeted at TRON’s founder, Justin Sun. Notably, in March, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) indicted Sun and three affiliated entities over alleged unauthorized crypto-asset dealings.
Top 5 Tokens using the TRC-20 Standard
- Tether (USDT)
- BitTorrent (BTT)
- JUST Network (JST)
- USDD (USDD)
- APENFT (NFT)
Decentralized Applications and Wallets Supporting TRC-20
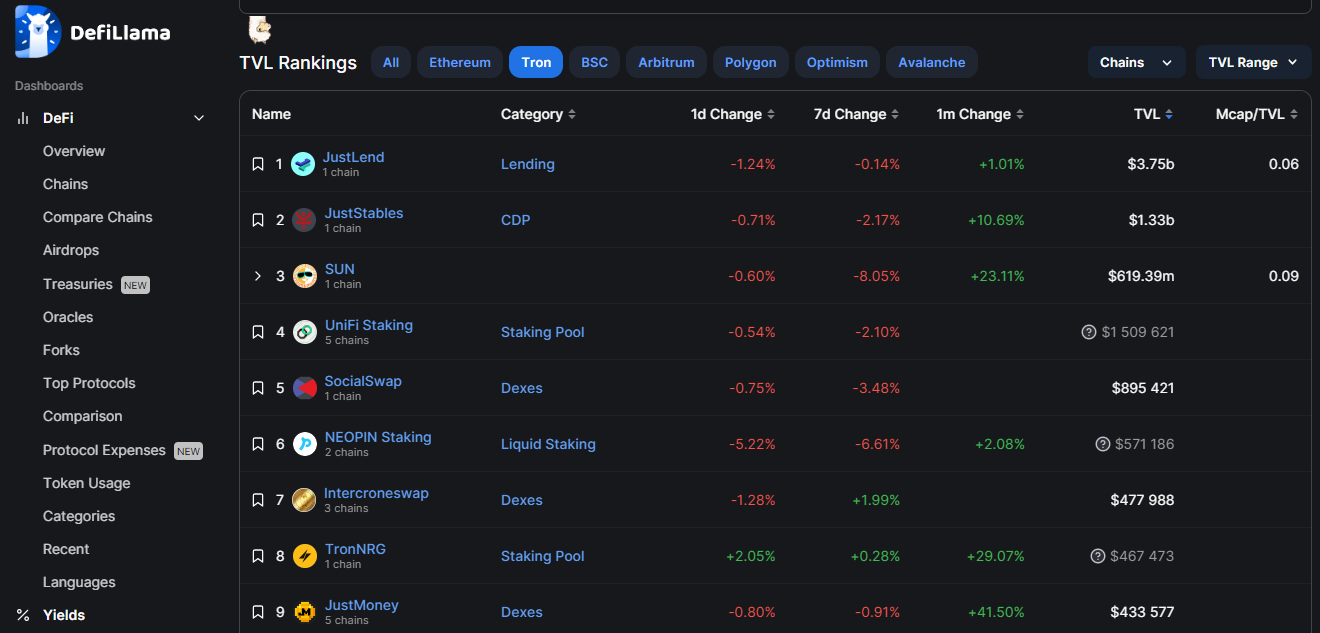
Top Apps by Locked-in Funds Volume
- JustLend
- JustStable
- SUN
- UniFi
- SocialSwap
Non-custodial Wallets for TRC-20
- TronLink
- Trust Wallet
- Atomic Wallet
- MathWallet
- imToken
TRC-20 Token Explorers
- Tronscan
- Oklink
- Bitquery