allowing one blockchain’s native token to be exchanged for its equivalent on another.
For instance, using a cross-chain bridge, you can move ETH from the Ethereum network to Polygon, where it’s typically represented as wETH (wrapped ETH) or an equivalent. This allows you to utilize Ethereum’s assets within the Polygon ecosystem without using the services of a DEX. Likewise, you can transfer USDT from Ethereum to Polygon, obtaining a wrapped or pegged version on the Polygon side. This strategy lets you remain within the same asset class, mitigating risks associated with currency fluctuations.
We advise using cross-chain bridges only for those who fully understand their benefits and drawbacks. This is because transferring between networks can result in substantial fees. Consequently, it’s often more cost-effective to move assets through centralized exchanges (like Binance, ByBit, KuCoin, OKX, and others). If you wish to transfer funds from Ethereum to Polygon, the most economical method would typically involve first depositing assets into an exchange, possibly conducting a trade, and then withdrawing to Polygon. This process would typically incur no more than $3 in transaction fees alone (excluding exchange fees for trading, which usually hovers around 0.1%). Clearly, for the average user, using bridges isn’t beneficial.
Who opts for cross-chain bridges? It’s often large traders or investors distrustful of centralized exchanges. Such individuals are unwilling to bear the risk associated with lost or withheld funds, or they may want to remain anonymous (major exchanges usually require KYC verification).
How Cross-Chain Bridges Work
While many popular protocols have technical differences, at a high level, they share many similarities.
Typically, a bridge operates on the following principle:
- The user sends tokens (like USDT) to a smart contract, where they are frozen.
- A proportionate amount of wrapped tokens is minted in the target blockchain (say, Wrapped USDT).
- These are then swapped for an equivalent amount of liquid tokens via a specially designated liquidity pool (a WUSDT — USDT pair).
Currently, technology from LayerZero is gaining traction, enabling operations without intermediary tokens (in this case, Wrapped USDT).
In traditional cross-chain bridges, two liquid pairs must be created for each route (like WUSDT-USDT on both Ethereum and Polygon). This poses a scaling challenge—if another network is added, liquid pairs for every blockchain are necessary. Moving large balances becomes impractical due to limited liquidity.
LayerZero addresses this challenge by creating unified liquidity. You simply send a token into the liquidity pool on one blockchain (like Ethereum) and receive its equivalent on another (like Polygon). As a result, there only needs to be one liquidity pool per blockchain, greatly benefiting both liquidity providers and bridge users (like large traders).
Types of Bridges
Standalone Bridges
These projects specialize in covering as many networks as possible and earn their revenue from transaction fees. Examples include Stargate, Hyphen, Synapse, Chainswap, cBridge, and others.
Official L2 Network Bridges
These bridges work with only two networks — Ethereum and an L2 network. Such bridges are available with ZKSync, Optimism, Arbitrum, and others.
Bridge Comparison
In this article, we will focus specifically on standalone bridges, as they can be compared. We will compare the performance of different projects when transferring USDT from Ethereum to Polygon and vice versa.
We will compare them based on the following criteria:
- Total commission for transferring funds.
- Speed of fund delivery.
- Ease of use.
We will compare the operation of four popular cross-chain bridges under the same conditions: transferring 100 USDT from the Ethereum network to Polygon and back. We chose these blockchains for a reason — in the first one, we expect high fees, while Polygon is known for its moderately slow operation.
Stargate Finance
This is a project that uses LayerZero technology.
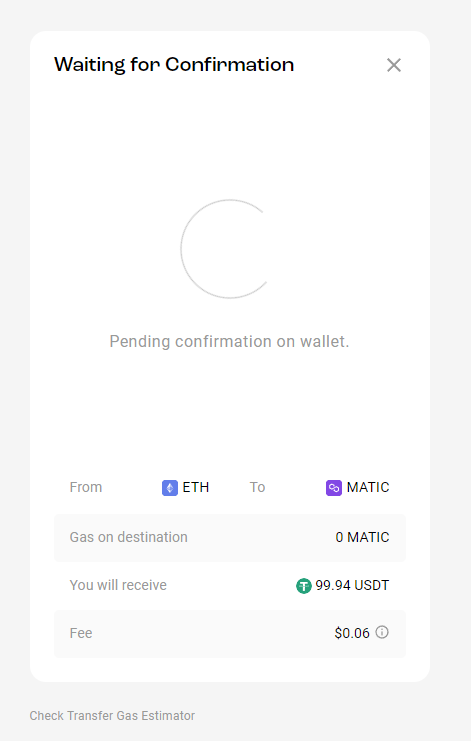
Stargate charges a fee of 0.04% of the transfer amount, and the website warns about this before the transaction is made. After confirming the transfer, we can see how much time is left before the funds arrive on the recipient blockchain.
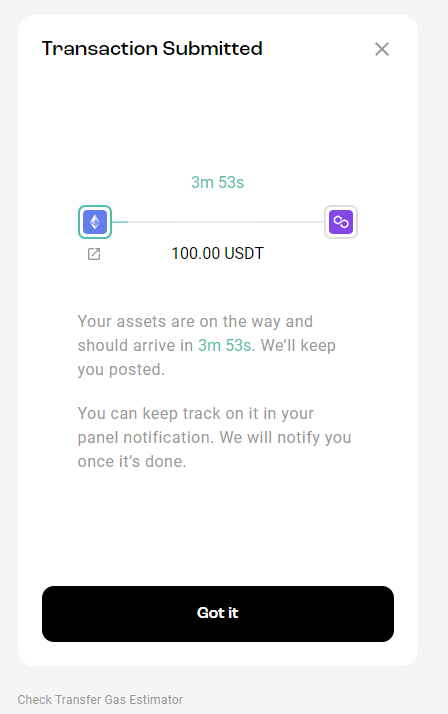
Stargate promises to transfer funds from Ethereum to Polygon in 4 minutes. Let’s check if this is true.
The funds arrived in 3 minutes and 45 seconds.
The network fee was about $22 with a gas price of 32 gwei. We will compare the Ethereum fee more precisely at the end of the article. Also, $1 goes to one of the LayerZero addresses, presumably for expenses on the Polygon network fee, which is a lot for this network.
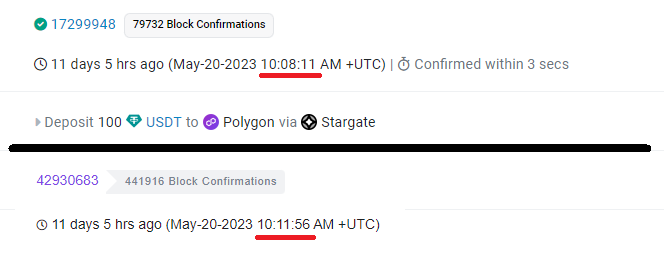
Next, we’ll make a transfer from Polygon.
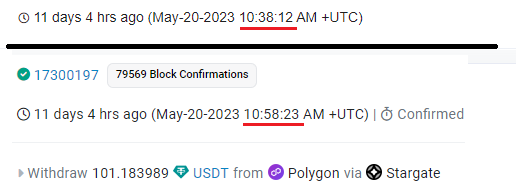
The entire process took 20 minutes and 11 seconds. It’s important to note that despite the small fees on the Polygon network, the bridge charges a fee denominated in MATIC to cover fees on the Ethereum network. In our case, ~$23 was spent.
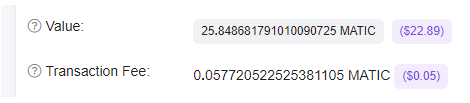
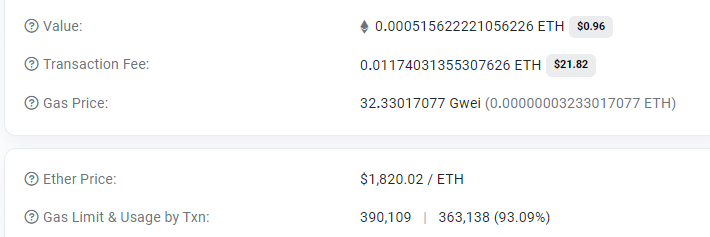
Let’s see how much was actually spent on the Ethereum fee:

It turns out that the protocol took us around $6 from us.
The overall impression from using the Stargate bridge remained positive — the website works well and even shows the time until the transfer is completed. As we’ll find out later, this feature is not available on any other bridge.
Synapse
This bridge also operates on the principle of wrapped tokens.
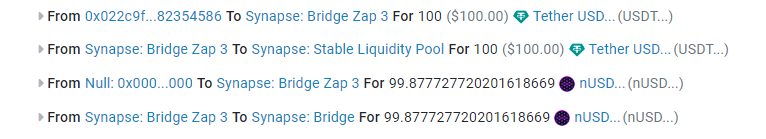
$99.5 arrived in the destination blockchain, but in terms of percentage, the service almost doesn’t take a commission. If we were to transfer $1000, even a smaller amount would go to the protocol.
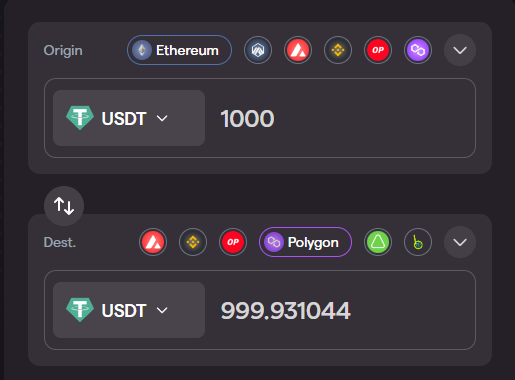
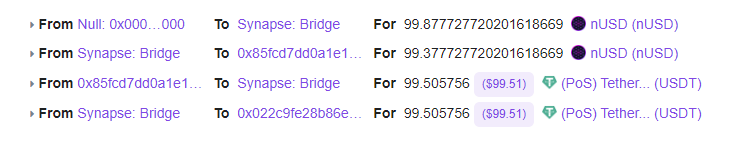
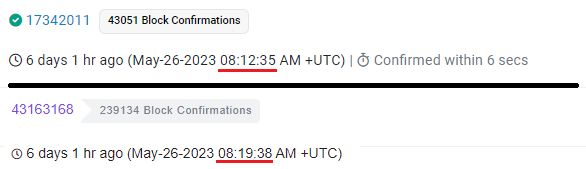
The transfer from Ethereum to Polygon took 7 minutes and 3 seconds.
Now, the transfer from Polygon.
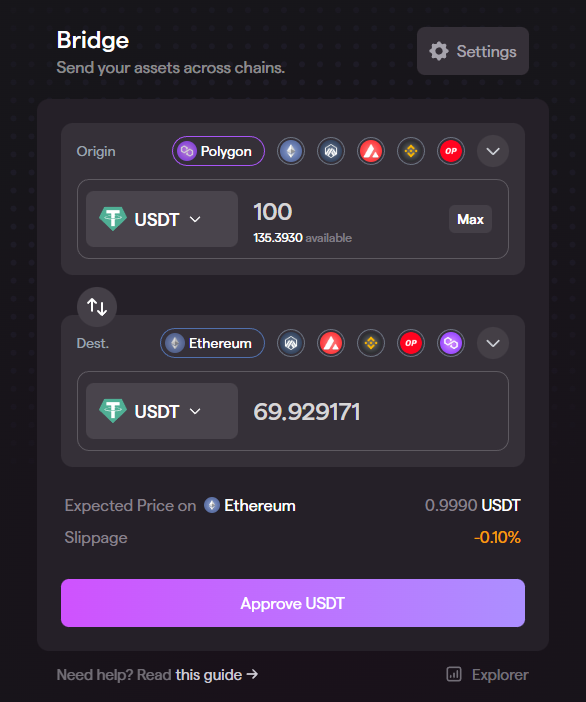
The service instantly notifies about a $30 fee.
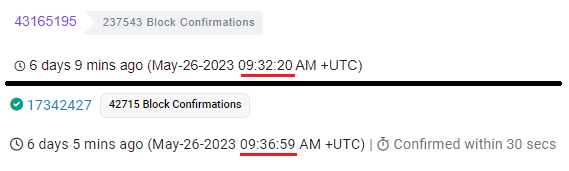
The transfer from Polygon took just 4 minutes and 39 seconds.

The service spent $13.39 on the Ethereum commission, earning $16.6 from this transaction.
cBridge (Celer)
This bridge supports 45 blockchains—a feat few services can match. However, it’s quite possible that you won’t use all the available networks, even if needed, since the protocol might lack liquidity for transferring larger balances. It’s far more efficient to operate through exchanges when dealing with less popular blockchains.
When transferring from Ethereum, the fee was reasonably low.
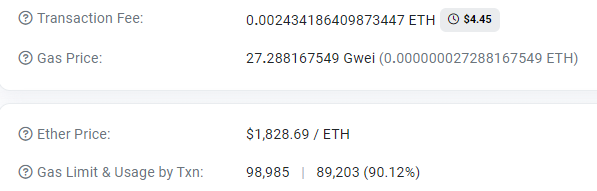
The service charged a mere $0.05 as a fee, which covers the transfer commission for Polygon. This means the project didn’t earn anything from the Ethereum transfer.
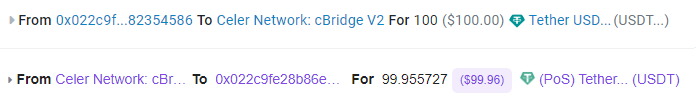
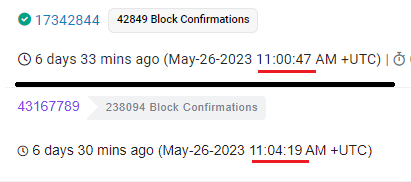
The entire transfer took 3 minutes and 32 seconds.
Now, we transfer from Polygon to Ethereum. Before transferring, the bridge indicates how much will be deducted for the fee. This time, they charged us $40.35.

It’s worth noting that this is a fixed fee for transferring to Ethereum. So, even for a transfer of $10,000, the service takes around 40-50 dollars.
However, the bridge only spent $9.76 on the fee.

This implies that for a transfer to Ethereum, the service earns $30—more than other cross-chain bridges in this review.
The operation took 8 minutes and 28 seconds.

cBridge demonstrated mixed results: on one hand, the absence of a fee when transferring from Ethereum was a pleasant surprise, and the transaction within this network was inexpensive. However, when transferring back, the service imposed a very high fee.
Conclusion
Now, let’s compare the bridges to determine the best one we’ve tested.
Cost of transferring from Ethereum:
Gas amount (cost at 30 gwei and Ethereum price at $1800) + bridge commission.
Stargate — 363138 ($19.6) + 0.04% + $1 goes to Polygon’s fee.
Synapse — 239749 ($12.94) + up to 0.50% (considering Polygon’s fee).
cBridge — 89203 ($4.81) + 0.05% (accounting for Polygon’s fee). It’s worth noting that the fee here fluctuates and seems to depend on liquidity.
Transfer speed from Ethereum to Polygon:
Stargate — 3 minutes 45 seconds.
Synapse — 7 minutes 3 seconds.
cBridge — 3 minutes 32 seconds.
Fee for transferring from Polygon to Ethereum:
Stargate — variable and depends on the destination blockchain’s fee, asking for a slightly higher amount than required. In our example, it’s $23.
Synapse — fixed at ~$30.
cBridge — fixed at ~$40.
Transfer speed from Polygon to Ethereum:
Stargate — 20 minutes 11 seconds.
Synapse — 4 minutes 39 seconds.
cBridge — 8 minutes 28 seconds.
Based on the analysis, the following conclusions can be made:
- cBridge is the fastest for transfers from Ethereum, with the lowest fees.
- The fairest fee for transferring to Ethereum is offered by Stargate.
- Synapse works the fastest on Polygon.
- Stargate provides the most user-friendly interface. No other bridge indicates an approximate delivery time for funds.
The accuracy of this review can be verified on Polygonscan and Etherscan.
